As we ring in 2025, Cancer Research Catalyst wishes you a very Happy New Year! May your 2025 be full of love, connection, and inspiration. As always, we love to keep you connected with inspiring cancer research by sharing this month’s editors’ picks from the 10 American Association for Cancer Research (AACR) journals. December’s holiday hits included two articles about immunosuppression in the lung, mathematical models that can predict adenoma progression and optimize radionuclide therapy, two clinical trials, and more.
These articles, like our holiday cheer, will remain freely available for a limited time.
Journal: Blood Cancer Discovery
A View of Myeloid Transformation through the Hallmarks of Cancer
The development of myeloid malignancies is influenced by a range of cell-intrinsic and cell-extrinsic factors, which can be conceptualized using the hallmarks of cancer. Although many facets of myeloid transformation are similar to those in solid tumors, there are also notable differences. Unlike solid tumors, hematologic malignancies typically exhibit fewer genetic mutations, which have been well characterized. However, understanding the cell-extrinsic factors contributing to myeloid malignancies can be challenging due to the complex interactions in the hematopoietic microenvironment. Researchers need to focus on these intricate factors to prevent the early onset of myeloid transformation and develop appropriate interventions.
Significance: Myeloid malignancies are common in the elderly, and acute myeloid leukemia has an adverse prognosis in older patients. Investigating cell-extrinsic factors influencing myeloid malignancies is crucial to developing approaches for preventing or halting disease progression and predicting clinical outcomes in patients with advanced disease. Whereas successful intervention may require targeting various mechanisms, understanding the contribution of each cell-extrinsic factor will help prioritize clinical targets.
This article is part of a Cancer Hallmarks article collection compiled by the AACR journals.
Journal: Cancer Discovery
MARK2/MARK3 Kinases Are Catalytic Codependencies of YAP/TAZ in Human Cancer
The Hippo signaling pathway is commonly dysregulated in human cancer, which leads to a powerful tumor dependency on the YAP/TAZ transcriptional coactivators. In this study, we used paralog cotargeting CRISPR screens to identify kinases MARK2/3 as absolute catalytic requirements for YAP/TAZ function in diverse carcinoma and sarcoma contexts. Underlying this observation is the direct MARK2/3-dependent phosphorylation of NF2 and YAP/TAZ, which effectively reverses the tumor suppressive activity of the Hippo module kinases LATS1/2. To simulate targeting of MARK2/3, we adapted the CagA protein from Helicobacter pylori as a catalytic inhibitor of MARK2/3, which we show can regress established tumors in vivo. Together, these findings reveal MARK2/3 as powerful codependencies of YAP/TAZ in human cancer, targets that may allow for pharmacology that restores Hippo pathway–mediated tumor suppression.
Significance: We show how genetic redundancy conceals tight functional relationships between signaling and transcriptional activation in cancer. Blocking the function of MARK2/3 kinases leads to the reactivation of the Hippo tumor suppressive pathway and may have therapeutic potential in YAP/TAZ-dysregulated carcinomas and sarcomas.
A related commentary was published in the December issue, where this study was also featured on the cover.
Journal: Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention
High Incidence of Gastric Cancer in El Salvador: A National Multisectorial Study during 2000 to 2014
Background: Gastric adenocarcinoma is the fourth leading cause of global cancer mortality and leading infection-associated cancer. Gastric cancer has significant geographic variability, with a high incidence in East Asia and mountainous regions of Latin America. In the United States, gastric cancer represents a marked disparity with incidence rates that are two to three times higher in Hispanics compared to non-Hispanic Whites.
Methods: We conducted a national retrospective study of incident gastric cancer in El Salvador from to 2000 to 2014 to estimate the age-standardized incidence rate (ASIR) by using a combination of pathology and endoscopy databases. A unique multisectorial coalition was formed between the Ministry of Health (MINSAL) and ES Gastroenterology Society (AGEDES), representing public hospitals (n = 5), governmental employee hospitals (ISSS, n = 5), and private facilities (n = 6), accounting for >95% of national endoscopy capacity. HER2 and EBV tumor status was ascertained in a representative sample during 2014 to 2016.
Results: A total of 10,039 unique cases of gastric cancer were identified, 45.5% female, and mean age of 65. 21% and 9.4% were <55 and <45 years old, respectively. ASIRs (M, F) were 18.9 (95% CI, 14.4–20.7) and 12.2 per 100,000 persons (95% CI, 10.9–13.5), respectively, in the period 2010 to 2014 with all centers operational. Intestinal gastric cancer was 2.8 times more common than diffuse gastric cancer; 23.2% had partial or complete pyloric obstruction. The HER2 2+/3+ status was 16.7% and EBV-encoded RNA positivity was 10.2%.
Conclusions: A high incidence of gastric cancer was confirmed in El Salvador and nearly half of the patients were female.
Impact: The findings have implications for cancer control in the Central America LMICs and for US Latino populations.
A related commentary was published in the December issue, where this article was also highlighted.
Journal: Cancer Immunology Research
Inflammation Mediated by Gut Microbiome Alterations Promotes Lung Cancer Development and an Immunosuppressed Tumor Microenvironment
Accumulating evidence indicates that the gut microbiome influences cancer progression and therapy. We recently showed that progressive changes in gut microbial diversity and composition are closely coupled with tobacco-associated lung adenocarcinoma in a human-relevant mouse model. Furthermore, we demonstrated that the loss of the antimicrobial protein Lcn2 in these mice exacerbates protumor inflammatory phenotypes while further reducing microbial diversity. Yet, how gut microbiome alterations impinge on lung adenocarcinoma development remains poorly understood. In this study, we investigated the role of gut microbiome changes in lung adenocarcinoma development using fecal microbiota transfer and delineated a pathway by which gut microbiome alterations incurred by loss of Lcn2 fostered the proliferation of proinflammatory bacteria of the genus Alistipes, triggering gut inflammation. This inflammation propagated systemically, exerting immunosuppression within the tumor microenvironment, augmenting tumor growth through an IL6-dependent mechanism and dampening response to immunotherapy. Corroborating our preclinical findings, we found that patients with lung adenocarcinoma with a higher relative abundance of Alistipes species in the gut showed diminished response to neoadjuvant immunotherapy. These insights reveal the role of microbiome-induced inflammation in lung adenocarcinoma and present new potential targets for interception and therapy.
Journal: Cancer Prevention Research
Construction and Validation of a Novel Forecasting Nomogram to the Risk of Colorectal Adenomas: Preventing Colorectal Cancer at Its Origin
Colorectal adenomas are responsible for the origin of most colorectal cancers. Early detection together with active intervention of colorectal adenomas plays a crucial role in the prevention of colorectal cancer. This study aimed to construct and validate a new nomogram for the forecasting of the risk of colorectal adenomas based on lifestyle risk factors that could offer potential benefits for colorectal cancer prevention. Colonoscopy reports, pathology reports, physical factors, family history, personal history of disease, diet, and lifestyle habits were collected from 1,133 subjects who underwent complete colonoscopy. All subjects were divided into the training cohort (n = 792) and the validation cohort (n = 341). A nomogram predicting the risk of colorectal adenoma development was constructed using the training cohort, and the C-index was calculated. The predictive accuracy and clinical applicability of the nomogram were verified in the validation cohort. The nomogram was constructed by six statistically significant variables selected from 18 health factors, including advanced age, male, smoking, drinking, pickles, and irregular defecation. The C-index of the training cohort was 0.778, and the C-index of the validation cohort was 0.754. The calibration curve and decision curve analysis also confirmed that the model has good predictive ability and high profit. The nomogram constructed in this study was validated and can be applied to predicting the occurrence risk of colorectal adenoma. The model can guide the identification of patients with nonsymptomatic colorectal adenomas and the recognition of high-risk individuals for whom colonoscopy is advisable.
Prevention Relevance: Colorectal adenomas are the origin of most colorectal cancers. In this research, we explored the risk factors of colorectal adenomas and constructed a colorectal adenoma risk prediction nomogram in the expectation of early detection of patients with nonsymptomatic colorectal adenoma and advocated for their aggressive treatment to achieve colorectal cancer prevention.
Journal: Cancer Research (December 1 issue)
Single-Cell Transcriptomic Analysis Identifies Senescent Osteocytes That Trigger Bone Destruction in Breast Cancer Metastasis
Breast cancer bone metastases increase fracture risk and are a major cause of morbidity and mortality among women. Upon colonization by tumor cells, the bone microenvironment undergoes profound reprogramming to support cancer progression, which disrupts the balance between osteoclasts and osteoblasts and leads to bone lesions. A deeper understanding of the processes mediating this reprogramming could help develop interventions for treating patients with bone metastases. Here, we demonstrated that osteocytes (Ot) in established breast cancer bone metastasis develop premature senescence and a distinctive senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP) that favors bone destruction. Single-cell RNA sequencing identified Ots from mice with breast cancer bone metastasis enriched in senescence, SASP markers, and pro-osteoclastogenic genes. Multiplex in situ hybridization and artificial intelligence–assisted analysis depicted Ots with senescence-associated satellite distension, telomere dysfunction, and p16Ink4a expression in mice and patients with breast cancer bone metastasis. Breast cancer cells promoted Ot senescence and enhanced their osteoclastogenic potential in in vitro and ex vivo organ cultures. Clearance of senescent cells with senolytics suppressed bone resorption and preserved bone mass in mice with breast cancer bone metastasis. These results demonstrate that Ots undergo pathological reprogramming by breast cancer cells and identify Ot senescence as an initiating event triggering lytic bone disease in breast cancer metastases.
Significance: Breast cancer cells remodel the bone microenvironment by promoting premature cellular senescence and SASP in osteocytes, which can be targeted with senolytics to alleviate bone loss induced by metastatic breast cancer.
A related commentary was published in the December issue.
Journal: Cancer Research (December 15 issue)
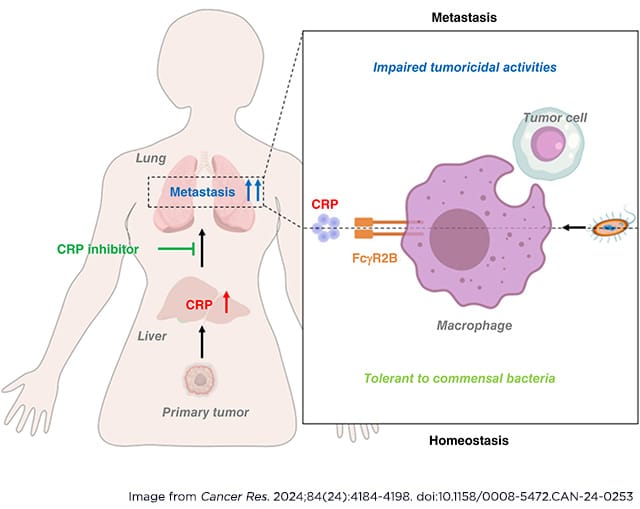
C-Reactive Protein Induces Immunosuppression by Activating FcγR2B in Pulmonary Macrophages to Promote Lung Metastasis
C-reactive protein (CRP) is a liver-derived acute phase reactant that is a clinical marker of inflammation associated with poor cancer prognosis. Elevated CRP levels are observed in many types of cancer and are associated with significantly increased risk of metastasis, suggesting that CRP could have prometastatic actions. In this study, we reported that CRP promotes lung metastasis by dampening the anticancer capacity of pulmonary macrophages in breast cancer and melanoma. Deletion of CRP in mice inhibited lung metastasis of breast cancer and melanoma cells without significantly impacting tumor growth compared with wild-type mice. In addition, the lungs of CRP-deficient mice were enriched for activated pulmonary macrophages, which could be reduced to the level of wild-type mice by systemic administration of human CRP. Mechanistically, CRP blocked the activation of pulmonary macrophages induced by commensal bacteria in a FcγR2B-dependent manner, thereby impairing macrophage-mediated immune surveillance to promote the formation of a premetastatic niche in the lungs of tumor-bearing mice. Accordingly, treatment with specific CRP inhibitors activated pulmonary macrophages and attenuated lung metastasis in vivo. These findings highlight the importance of CRP in lung metastasis, which may represent an effective therapeutic target for patients with advanced solid cancers in clinics.
Significance: CRP maintains host–commensal tolerance by inhibiting pulmonary macrophage activation and can be targeted to remodel the premetastatic niche in the lung to lower the risk of cancer metastasis.
A related commentary was published in the December issue.
Journal: Clinical Cancer Research (December 1 issue)
Efficacy and Safety of the Anti-IL1RAP Antibody Nadunolimab (CAN04) in Combination with Gemcitabine and Nab-Paclitaxel in Patients with Advanced/Metastatic Pancreatic Cancer
Purpose: IL1 pathway upregulation is implicated in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) progression, therapy resistance, and survival. Nadunolimab is an IL1 receptor accessory protein (IL1RAP)–targeting antibody with enhanced antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity that blocks IL1α/IL1β signaling. We investigated efficacy and safety of nadunolimab in PDAC, in combination with gemcitabine/nab-paclitaxel (GN).
Patients and Methods: Patients with previously untreated locally advanced/metastatic PDAC received nadunolimab (1.0–7.5 mg/kg) every 2 weeks with standard GN. The primary objective was safety; secondary objectives were antitumor response, progression-free survival, and overall survival (OS). Correlations between serum and tumor biomarkers and clinical response were explored.
Results: Seventy-six patients were enrolled; the median age was 63 years (range, 43–89), 42% were female, 97% had metastatic disease, and 9% had received adjuvant chemotherapy. The most frequent grade ≥3 adverse event was neutropenia (66%), typically during cycle 1. Infusion-related reactions occurred in 29% (grade 3, 3%). Only 1 of the 76 patients had grade 3 or above peripheral neuropathy. No marked dose-dependent differences in safety or efficacy were observed among the four dose groups. The median OS was 13.2 months (95% confidence interval, 11.0–15.6), and the 1-year survival rate was 58%. The median immune PFS (immune Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumours) was 7.1 months (95% confidence interval, 5.2–7.4). Treatment efficacy was higher in patients with high versus low tumor baseline IL1RAP expression (OS 14.2 vs. 10.6 months; P = 0.012). A reduction in serum IL8 on treatment correlated with prolonged OS.
Conclusions: Nadunolimab combined with GN shows promising efficacy and manageable safety in locally advanced/metastatic PDAC. Higher tumor baseline IL1RAP expression correlated with better outcome.
Journal: Clinical Cancer Research (December 15 issue)
Trastuzumab Deruxtecan with Nivolumab in HER2-Expressing Metastatic Breast or Urothelial Cancer: Analysis of the Phase Ib DS8201-A-U105 Study
Purpose: This multicenter phase Ib study investigated trastuzumab deruxtecan (T-DXd) plus nivolumab in patients with HER2-expressing metastatic breast cancer (mBC) and metastatic urothelial cancer (mUC).
Patients and Methods: Part 1 determined the recommended dose for expansion of T-DXd plus nivolumab. Part 2 evaluated efficacy and safety; the primary endpoint was confirmed objective response rate by independent central review.
Results: In part 1, seven patients with mBC were enrolled and received T-DXd 3.2 mg/kg (four patients) or 5.4 mg/kg (three patients) plus nivolumab. The recommended dose for expansion for T-DXd was 5.4 mg/kg plus nivolumab 360 mg intravenously every 3 weeks. In part 2, 32 patients with HER2-positive mBC (cohort 1; inclusive of three administered 5.4 mg/kg in part 1), 16 with HER2-low mBC (cohort 2), 30 with HER2-high mUC (cohort 3), and four with HER2-low mUC (cohort 4) were enrolled. At data cutoff (July 22, 2021), the confirmed objective response rates (95% confidence interval) for cohorts 1 to 4 were 65.6% (46.8%−81.4%), 50.0% (24.7%−75.3%), 36.7% (19.9%−56.1%), and not assessed due to small sample size, respectively. The median treatment duration (range) with T-DXd in cohorts 1 to 4 was 8.9 (1–23) months, 6.9 (1–21) months, 3.9 (1–21) months, and not assessed, respectively; the most common treatment-emergent adverse event was nausea (55.2%, 62.5%, 73.3%, and 75.0%, respectively). Adjudicated drug-related interstitial lung disease/pneumonitis rates (cohorts 1–3) were 20.7%, 0%, and 20.0%, respectively (one grade 5 each, cohorts 1 and 3).
Conclusions: T-DXd plus nivolumab demonstrated promising antitumor activity in HER2-expressing mBC or mUC and safety consistent with the known profile of T-DXd. Interstitial lung disease/pneumonitis is an important risk and requires careful monitoring and prompt intervention.
Journal: Molecular Cancer Research
Defining Splicing Factor Requirements for Androgen Receptor Variant Synthesis in Advanced Prostate Cancer
Resistance to androgen receptor (AR)–targeted therapies represents a major challenge in prostate cancer. A key mechanism of treatment resistance in patients who progress to castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC) is the generation of alternatively spliced AR variants (AR-V). Unlike full-length AR isoforms, AR-Vs are constitutively active and refractory to current receptor-targeting agents and hence drive tumor progression. Identifying regulators of AR-V synthesis may therefore provide new therapeutic opportunities in combination with conventional AR-targeting agents. Our understanding of AR transcript splicing, and the factors that control the synthesis of AR-Vs, remains limited. Although candidate-based approaches have identified a small number of AR-V splicing regulators, an unbiased analysis of splicing factors important for AR-V generation is required to fill an important knowledge gap and furnish the field with novel and tractable targets for prostate cancer treatment. To that end, we conducted a bespoke CRISPR screen to profile splicing factor requirements for AR-V synthesis. MFAP1 and CWC22 were shown to be required for the generation of AR-V mRNA transcripts, and their depletion resulted in reduced AR-V protein abundance and cell proliferation in several CRPC models. Global transcriptomic analysis of MFAP1-depleted cells revealed both AR-dependent and -independent transcriptional impacts, including genes associated with DNA damage response. As such, MFAP1 downregulation sensitized prostate cancer cells to ionizing radiation, suggesting that therapeutically targeting AR-V splicing could provide novel cellular vulnerabilities which can be exploited in CRPC.
Implications: We have utilized a CRISPR screening approach to identify key regulators of pathogenic AR splicing in prostate cancer.
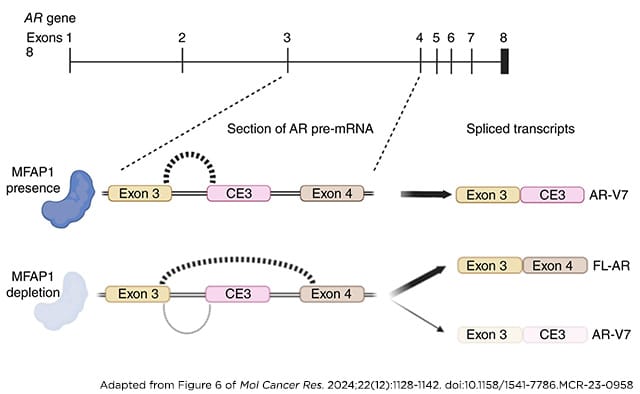
This study was highlighted in the December issue.
Journal: Molecular Cancer Therapeutics
Discovery of RGT-018: A Potent, Selective, and Orally Bioavailable SOS1 Inhibitor for KRAS-Driven Cancers
KRAS is the most frequently dysregulated oncogene with a high prevalence in non–small cell lung cancer, colorectal cancer, and pancreatic cancer. FDA-approved sotorasib and adagrasib provide breakthrough therapies for patients with cancer with KRASG12C mutation. However, there is still high unmet medical need for new agents targeting broader KRAS-driven tumors. An emerging and promising opportunity is to develop a pan KRAS inhibitor by suppressing the upstream protein of Son of Sevenless 1 (SOS1). SOS1 is a key activator of KRAS and facilitates the conversion of GDP-bound KRAS state to GTP-bound KRAS state. Binding to its catalytic domain, small-molecule SOS1 inhibitor has demonstrated the ability to suppress KRAS activation and cancer cell proliferation. RGT-018, a potent and selective SOS1 inhibitor, was identified with optimal drug-like properties. In vitro, RGT-018 blocked the interaction of KRAS:SOS1 with single-digit nanomoles per liter potency and was highly selective against SOS2. RGT-018 inhibited KRAS signaling and the proliferation of a broad spectrum of KRAS-driven cancer cells as a single agent in vitro. Further enhanced antiproliferation activity was observed when RGT-018 was combined with MEK, KRASG12C, EGFR, or CDK4/6 inhibitors. Oral administration of RGT-018 inhibited tumor growth and suppressed KRAS signaling in tumor xenografts in vivo. Combinations with MEK or KRASG12C inhibitors led to significant tumor regression. Furthermore, RGT-018 overcame the resistance to the approved KRASG12C inhibitors caused by clinically acquired KRAS mutations either as a single agent or in combination. RGT-018 displayed promising pharmacological properties for combination with targeted agents to treat a broader KRAS-driven patient population.
This study was highlighted in the December issue.
Journal: Cancer Research Communications
Mathematical Modeling Unveils Optimization Strategies for Targeted Radionuclide Therapy of Blood Cancers
Targeted radionuclide therapy (TRT) is based on injections of cancer-specific molecules conjugated with radioactive nuclides. Despite the specificity of this treatment, it is not devoid of side effects limiting its use and is especially harmful for rapidly proliferating organs well perfused by blood, like bone marrow. Optimization of radioconjugate administration accounting for toxicity constraints can increase treatment efficacy. Based on our experiments on a disseminated multiple myeloma mouse model treated by 225Ac-DOTA-daratumumab, we developed a mathematical model, investigation of which highlighted the following principles for optimization of TRT: (i) Nuclide-to-antibody ratio importance. The density of radioconjugates on cancer cells determines the density of radiation energy deposited in them. A low labeling ratio as well as accumulation of unlabeled antibodies and antibodies attached to decay products in the bloodstream can mitigate cancer radiation damage due to excessive occupation of specific receptors by antibodies devoid of radioactive nuclides. (ii) Cancer-binding capacity–based dosing. The total number of specific receptors on cancer cells is a critical factor for treatment optimization, and its estimation may allow increasing treatment efficacy close to its theoretical limit. Injection of doses significantly exceeding cancer-binding capacity should be avoided because radioconjugates remaining in the bloodstream have a negligible efficacy-to-toxicity ratio. (iii) Particle range–guided multi-dosing. The use of short-range particle emitters and high-affinity antibodies can allow for robust treatment optimization via initial saturation of cancer-binding capacity, enabling redistribution of further injected radioconjugates and deposited doses toward still viable cells that continue expressing specific receptors.
Significance: Mathematical modeling yields general principles for optimization of TRT in mouse models of multiple myeloma that can be extrapolated to other cancer models and clinical settings.


