As a weekend of barbecues and fireworks looms on the horizon, the editors of the 10 American Association for Cancer Research (AACR) journals are serving up some sizzling cancer research published during the month of June. This month’s explosive articles include data from a phase III clinical trial leading to a new U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval for the KRAS inhibitor adagrasib; a new drug that may boost multiple other therapies; a way to predict chemotherapy response in glioblastoma using imaging; and more.
Like the United States, these articles are free—but only for a limited time. Check out the abstracts of this month’s picks below.
Journal: Blood Cancer Discovery
Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia with Myeloid Mutations Is a High-Risk Disease Associated with Clonal Hematopoiesis
Myeloid neoplasms arise from preexisting clonal hematopoiesis (CH); however, the role of CH in the pathogenesis of acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) is unknown. We found that 18% of adult ALL cases harbored TP53, and 16% had myeloid CH-associated gene mutations. ALL with myeloid mutations (MyM) had distinct genetic and clinical characteristics, associated with inferior survival. By using single-cell proteogenomic analysis, we demonstrated that myeloid mutations were present years before the diagnosis of ALL, and a subset of these clones expanded over time to manifest as dominant clones in ALL. Single-cell RNA sequencing revealed upregulation of genes associated with cell survival and resistance to apoptosis in B-ALL with MyM, which responds better to newer immunotherapeutic approaches. These findings define ALL with MyM as a high-risk disease that can arise from antecedent CH and offer new mechanistic insights to develop better therapeutic and preventative strategies.
Significance: CH is a precursor lesion for lymphoblastic leukemogenesis. ALL with MyM has distinct genetic and clinical characteristics, associated with adverse survival outcomes after chemotherapy. CH can precede ALL years before diagnosis, and ALL with MyM is enriched with activated T cells that respond to immunotherapies such as blinatumomab.
This study was featured on the cover of the May issue, and a related commentary is available here.
Journal: Cancer Discovery
Efficacy and Safety of Adagrasib plus Cetuximab in Patients with KRASG12C-Mutated Metastatic Colorectal Cancer
Adagrasib, an irreversible, selective KRASG12C inhibitor, may be an effective treatment in KRASG12C-mutated colorectal cancer, particularly when combined with an anti-EGFR antibody. In this analysis of the KRYSTAL-1 trial, patients with previously treated KRASG12C-mutated unresectable or metastatic colorectal cancer received adagrasib (600 mg twice daily) plus cetuximab. The primary endpoint was objective response rate (ORR) by blinded independent central review. Ninety-four patients received adagrasib plus cetuximab. With a median follow-up of 11.9 months, ORR was 34.0%, disease control rate was 85.1%, and median duration of response was 5.8 months (95% confidence interval [CI], 4.2–7.6). Median progression-free survival was 6.9 months (95% CI, 5.7–7.4) and median overall survival was 15.9 months (95% CI, 11.8–18.8). Treatment-related adverse events (TRAEs) occurred in all patients; grade 3–4 in 27.7% and no grade 5. No TRAEs led to adagrasib discontinuation. Exploratory analyses suggest circulating tumor DNA may identify features of response and acquired resistance.
Significance: Adagrasib plus cetuximab demonstrates promising clinical activity and tolerable safety in heavily pretreated patients with unresectable or metastatic KRASG12C-mutated colorectal cancer. These data support a potential new standard of care and highlight the significance of testing and identification of KRASG12C mutations in patients with colorectal cancer.
This study was highlighted and featured on the cover of the June issue, and the data were presented at the AACR Annual Meeting 2024. This month, the FDA also approved adagrasib plus cetuximab for use in patients with previously treated KRASG12C-mutated colorectal cancer.
Journal: Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention
Reproductive Factors Related to Childbearing and a Novel Automated Mammographic Measure, V
Background: We investigated the associations between several reproductive factors related to childbearing and the variation (V) measure (a novel, objective, single summary measure of breast image intensity) by menopausal status.
Methods: Our study included 3,814 cancer-free women within the Nurses’ Health Study (NHS) and NHSII cohorts. The data on reproductive variables and covariates were obtained from biennial questionnaires closest to the mammogram date. V-measures were obtained from mammographic images using a previously developed algorithm capturing the standard deviation of pixel values. We used multivariate linear regression to examine the associations of parity, age at first birth, time between menarche and first birth, time since last pregnancy, and lifetime breastfeeding duration with V-measure, adjusting for breast cancer risk factors, including the percentage of mammographic density (PMD). We further examined whether these associations were statistically accounted for (mediated) by PMD.
Results: Among premenopausal women, none of the reproductive factors were associated with V. Among postmenopausal women, inverse associations of parity and positive associations of age at first birth with V were mediated by PMD (percent mediated: nulliparity: 66.7%, P < 0.0001; parity: 50.5%, P < 0.01; age at first birth 76.1%, P < 0.001) and were no longer significant in PMD-adjusted models. Lifetime duration of breastfeeding was positively associated with V [>36 vs. 0 ≤1 months β = 0.29; 95% confidence interval (CI) 0.07; 0.52, Ptrend < 0.01], independent of PMD.
Conclusions: Parity, age at first birth, and breastfeeding were associated with postmenopausal V.
Impact: This study highlights associations of reproductive factors with mammographic image intensity.
This study was highlighted in the June issue.
Journal: Cancer Immunology Research
Unleashing Natural IL18 Activity Using an Anti-IL18BP Blocker Induces Potent Immune Stimulation and Antitumor Effects

Recombinant cytokines have limited anticancer efficacy mostly due to a narrow therapeutic window and systemic adverse effects. IL18 is an inflammasome-induced proinflammatory cytokine, which enhances T- and NK-cell activity and stimulates IFNγ production. The activity of IL18 is naturally blocked by a high-affinity endogenous binding protein (IL18BP). IL18BP is induced in the tumor microenvironment (TME) in response to IFNγ upregulation in a negative feedback mechanism. In this study, we found that IL18 is upregulated in the TME compared with the periphery across multiple human tumors and most of it is bound to IL18BP. Bound IL18 levels were largely above the amount required for T-cell activation in vitro, implying that releasing IL18 in the TME could lead to potent T-cell activation. To restore the activity of endogenous IL18, we generated COM503, a high-affinity anti-IL18BP that blocks the IL18BP:IL18 interaction and displaces precomplexed IL18, thereby enhancing T- and NK-cell activation. In vivo, administration of a surrogate anti-IL18BP, either alone or in combination with anti-PD-L1, resulted in significant tumor growth inhibition and increased survival across multiple mouse tumor models. Moreover, the anti-IL18BP induced pronounced TME-localized immune modulation including an increase in polyfunctional nonexhausted T- and NK-cell numbers and activation. In contrast, no increase in inflammatory cytokines and lymphocyte numbers or activation state was observed in serum and spleen. Taken together, blocking IL18BP using an Ab is a promising approach to harness cytokine biology for the treatment of cancer.
This study was featured on the cover of the June issue.
Journal: Cancer Prevention Research
Low-Carbohydrate Diet Score and Risk of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Findings from a Prospective Cohort Study
Limited data are reported on the association between low-carbohydrate diet (LCD) score, a comprehensive measure of dietary pattern according to sources of carbohydrate, fat, and protein, and risk of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). We evaluated this score with HCC risk in the Singapore Chinese Health Study, a prospective cohort of 63,275 middle-aged and elderly Chinese living in Singapore and recruited during 1993–1998 period. LCD scores were derived from the semi-quantitative food frequency questionnaire at baseline. A nested case–control study involved 197 HCC cases and 465 controls was also constructed among 28,346 participants who provided blood samples. Cox proportional hazard regression method was used to calculate HRs and 95% confidence intervals (CI) for HCC with different levels of LCD scores. Conditional logistic regression was performed for the case–control study analysis. After 17.6 years of follow-up with 819,573 person-years, 561 participants developed primary HCC. Although there was a null association between total LCD score and HCC risk (HRper-SD increment = 1.07; 95% CI, 0.98–1.16; Ptrend = 0.06), there was a positive association between animal-based LCD and the risk of HCC (HRper-SD increment = 1.11; 95% CI, 1.02–1.21; Ptrend = 0.01). Furthermore, this association was present in both HBsAg-negative and HBsAg-positive individuals in the case–control study. In stratified analysis for the entire cohort, this positive association was only present in those who consumed alcoholic beverages monthly or less frequent but not in weekly or daily drinker (Pinteraction = 0.79). In summary, a diet with lower carbohydrate, higher animal fat and protein was significantly associated with higher risk of HCC among Chinese Singaporeans.
Prevention Relevance: In a large cohort study of more than 63,000 Chinese Singaporeans, we found that a diet with lower carbohydrate and higher animal fat and protein was associated with increased risk of HCC, suggesting that dietary modification could be an effective strategy in primary prevention to reduce the HCC burden.
Journal: Cancer Research (June 1 issue)
Obesogenic High-Fat Diet and MYC Cooperate to Promote Lactate Accumulation and Tumor Microenvironment Remodeling in Prostate Cancer
Cancer cells exhibit metabolic plasticity to meet oncogene-driven dependencies while coping with nutrient availability. A better understanding of how systemic metabolism impacts the accumulation of metabolites that reprogram the tumor microenvironment (TME) and drive cancer could facilitate development of precision nutrition approaches. Using the Hi-MYC prostate cancer mouse model, we demonstrated that an obesogenic high-fat diet (HFD) rich in saturated fats accelerates the development of c-MYC–driven invasive prostate cancer through metabolic rewiring. Although c-MYC modulated key metabolic pathways, interaction with an obesogenic HFD was necessary to induce glycolysis and lactate accumulation in tumors. These metabolic changes were associated with augmented infiltration of CD206+ and PD-L1+ tumor-associated macrophages (TAM) and FOXP3+ regulatory T cells, as well as with the activation of transcriptional programs linked to disease progression and therapy resistance. Lactate itself also stimulated neoangiogenesis and prostate cancer cell migration, which were significantly reduced following treatment with the lactate dehydrogenase inhibitor FX11. In patients with prostate cancer, high saturated fat intake and increased body mass index were associated with tumor glycolytic features that promote the infiltration of M2-like TAMs. Finally, upregulation of lactate dehydrogenase, indicative of a lactagenic phenotype, was associated with a shorter time to biochemical recurrence in independent clinical cohorts. This work identifies cooperation between genetic drivers and systemic metabolism to hijack the TME and promote prostate cancer progression through oncometabolite accumulation. This sets the stage for the assessment of lactate as a prognostic biomarker and supports strategies of dietary intervention and direct lactagenesis blockade in treating advanced prostate cancer.
Significance: Lactate accumulation driven by high-fat diet and MYC reprograms the tumor microenvironment and promotes prostate cancer progression, supporting the potential of lactate as a biomarker and therapeutic target in prostate cancer.
Journal: Cancer Research (June 15 issue)
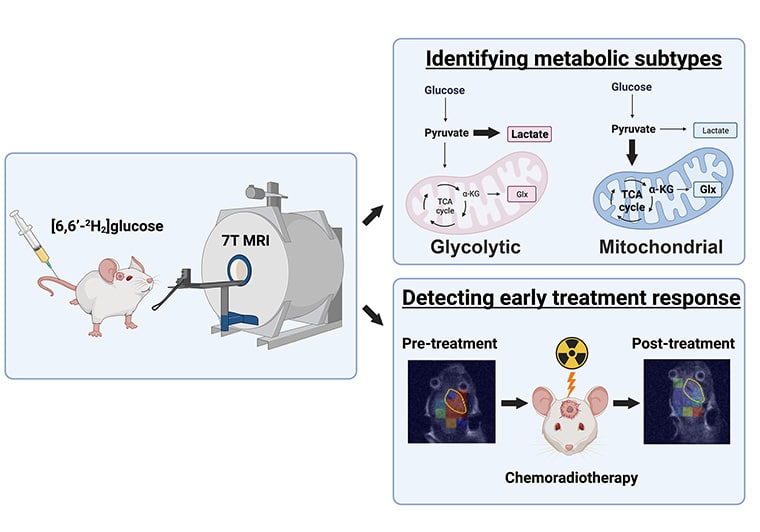
Deuterium Metabolic Imaging Differentiates Glioblastoma Metabolic Subtypes and Detects Early Response to Chemoradiotherapy
Metabolic subtypes of glioblastoma (GBM) have different prognoses and responses to treatment. Deuterium metabolic imaging with 2H-labeled substrates is a potential approach to stratify patients into metabolic subtypes for targeted treatment. In this study, we used 2H magnetic resonance spectroscopy and magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging (MRSI) measurements of [6,6′-2H2]glucose metabolism to identify metabolic subtypes and their responses to chemoradiotherapy in patient-derived GBM xenografts in vivo. The metabolism of patient-derived cells was first characterized in vitro by measuring the oxygen consumption rate, a marker of mitochondrial tricarboxylic acid cycle activity, as well as the extracellular acidification rate and 2H-labeled lactate production from [6,6′-2H2]glucose, which are markers of glycolytic activity. Two cell lines representative of a glycolytic subtype and two representative of a mitochondrial subtype were identified. 2H magnetic resonance spectroscopy and MRSI measurements showed similar concentrations of 2H-labeled glucose from [6,6′-2H2]glucose in all four tumor models when implanted orthotopically in mice. The glycolytic subtypes showed higher concentrations of 2H-labeled lactate than the mitochondrial subtypes and normal-appearing brain tissue, whereas the mitochondrial subtypes showed more glutamate/glutamine labeling, a surrogate for tricarboxylic acid cycle activity, than the glycolytic subtypes and normal-appearing brain tissue. The response of the tumors to chemoradiation could be detected within 24 hours of treatment completion, with the mitochondrial subtypes showing a decrease in both 2H-labeled glutamate/glutamine and lactate concentrations and glycolytic tumors showing a decrease in 2H-labeled lactate concentration. This technique has the potential to be used clinically for treatment selection and early detection of treatment response.
Significance: Deuterium magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging of glucose metabolism has the potential to differentiate between glycolytic and mitochondrial metabolic subtypes in glioblastoma and to evaluate early treatment responses, which could guide patient treatment.
Journal: Clinical Cancer Research (June 1 issue)
A Signal-Finding Study of Abemaciclib in Heavily Pretreated Patients with Metastatic Castration–Resistant Prostate Cancer: Results from CYCLONE 1
Purpose: Cyclin-dependent kinase 4 and 6 (CDK4/6) inhibitors radically changed the treatment paradigm for breast cancer. Similar to estrogen receptor in breast cancer, androgen receptor signaling activates cyclin D–CDK4/6, driving proliferation and resistance to hormonal manipulation in prostate cancer. This study was designed to detect signals of clinical activity for abemaciclib in treatment-refractory metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC).
Patients and Methods: Eligible patients had progressive mCRPC, measurable disease, and previously received ≥1 novel hormonal agent(s) and 2 lines of taxane chemotherapy. Abemaciclib 200 mg twice daily was administered on a continuous dosing schedule. Primary endpoint was objective response rate (ORR) without concurrent bone progression. This study was designed to detect a minimum ORR of 12.5%.
Results: At trial entry, 40 (90.9%) of 44 patients had objective radiographic disease progression, 4 (9.1%) had prostate-specific antigen (PSA)–only progression, and 20 (46.5%) had visceral metastases (of these, 60% had liver metastases). Efficacy analyses are as follows: ORR without concurrent bone progression: 6.8%; disease control rate: 45.5%; median time to PSA progression: 6.5 months [95% confidence interval (CI), 3.2–NA]; median radiographic PFS; 2.7 months (95% CI, 1.9–3.7); and median OS, 8.4 months (95% CI, 5.6–12.7). Most frequent grade ≥3 treatment-emergent adverse events (AE) were neutropenia (25.0%), anemia, and fatigue (11.4% each). No grade 4 or 5 AEs were related to abemaciclib.
Conclusions: Abemaciclib monotherapy was well tolerated and showed clinical activity in this heavily pretreated population, nearly half with visceral metastases. This study is considered preliminary proof-of-concept and designates CDK4/6 as a valid therapeutic target in prostate cancer.
This study was highlighted in the June 1 issue.
Journal: Clinical Cancer Research (June 15 issue)
A Phase I Trial of Nab-Paclitaxel/Bevacizumab (AB160) Nano-Immunoconjugate Therapy for Gynecologic Malignancies
Purpose: AB160 is a 160-nm nano-immunoconjugate consisting of nab-paclitaxel (ABX) nanoparticles noncovalently coated with bevacizumab (BEV) for targeted delivery into tissues expressing high levels of VEGF. Preclinical data showed that AB160 resulted in greater tumor targeting and tumor inhibition compared with sequential treatment with ABX then BEV. Given individual drug activity, we investigated the safety and toxicity of AB160 in patients with gynecologic cancers.
Patients and Methods: A 3+3 phase I trial was conducted with three potential dose levels in patients with previously treated endometrial, cervical, and platinum-resistant ovarian cancer to ascertain the recommended phase II dose (RP2D). AB160 was administered intravenously on days 1, 8, and 15 of a 28-day cycle (ABX 75–175 mg/m2, BEV 30–70 mg/m2). Pharmacokinetic analyses were performed.
Results: No dose-limiting toxicities (DLT) were seen among the three dose levels tested. Grade 3/4 toxicities included neutropenia, thromboembolic events, and leukopenia. DL2 (ABX 150 mg/m2, BEV 60 mg/m2) was chosen as the RP2D. Seven of the 19 patients with measurable disease (36.8%) had confirmed partial responses (95% confidence interval, 16.3%–61.6%). Pharmacokinetic analyses demonstrated that AB160 allowed 50% higher paclitaxel dosing and that paclitaxel clearance mirrored that of therapeutic antibodies.
Conclusions: The safety profile and clinical activity of AB160 supports further clinical testing in patients with gynecologic cancers; the RP2D is DL2 (ABX 150 mg/m2, BEV 60 mg/m2).
Journal: Molecular Cancer Research
FATP5 Is Indispensable for the Growth of Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma
Altered lipid metabolism is a common hallmark of various cancers, including intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICC), a highly lethal carcinoma that lacks effective treatment options. To elucidate the lipid metabolism changes in ICC, we coupled the expression of the firefly luciferase gene (FFL) to AKT1 (AKT-FFL) via an IRES linker, and then hydrodynamically injected mice with AKT-FFL and Notch1 intracellular cytoplasmic domain (NICD) to establish a luciferase-positive ICC model. This model not only enabled us to monitor and quantify tumor growth by injecting the mice with luciferin, but also allowed us to assess the fatty acid uptake rate by injecting the mice with free fatty acid luciferin (FFA-Luc). The ICC model exhibited robust uptake of exogenous fatty acids compared with the HCC model induced by AKT-FFL/ neuroblastoma Ras (Ras). Lipidomics analysis showed a dramatically higher level of fatty acid in ICC, further supporting the increased fatty acids uptake. Mechanistic studies identified FATP5 as the predominant mediator of fatty acid uptake required for ICC growth using Fatp5 knockout mice and AAV-based shRNA silencing of Fatp5. Our study discovered a novel therapeutic target for the treatment of ICC and shed light on the contributions of lipid metabolism to ICC development.
Implications: This study provides the first in vivo evidence that FATP5 is a potential therapeutic target for treating ICC.
This study was highlighted in the June issue.
Journal: Molecular Cancer Therapeutics
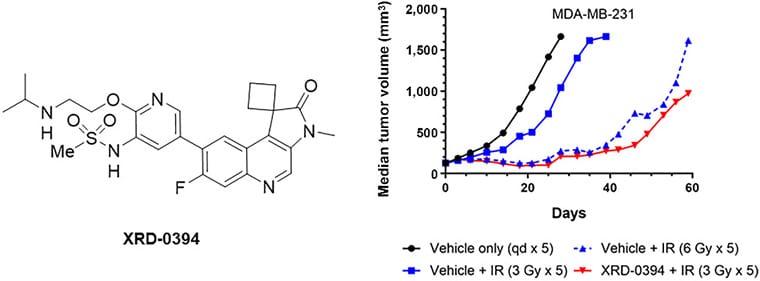
A Novel Dual ATM/DNA-PK Inhibitor, XRD-0394, Potently Radiosensitizes and Potentiates PARP and Topoisomerase I Inhibitors
A majority of patients with cancer receive radiotherapy as part of their treatment regimens whether using external beam therapy or locally-delivered radioisotopes. While often effective, some tumors are inadequately controlled with radiation and radiotherapy has significant short-term and long-term toxicities for cancer survivors. Insights into molecular mechanisms involved in cellular responses to DNA breaks introduced by radiation or other cancer therapies have been gained in recent years and approaches to manipulate these responses to enhance tumor cell killing or reduce normal tissue toxicity are of great interest. Here, we report the identification and initial characterization of XRD-0394, a potent and specific dual inhibitor of two DNA damage response kinases, ATM and DNA-PKcs. This orally bioavailable molecule demonstrates significantly enhanced tumor cell kill in the setting of therapeutic ionizing irradiation in vitro and in vivo. XRD-0394 also potentiates the effectiveness of topoisomerase I inhibitors in vitro. In addition, in cells lacking BRCA1/2 XRD-0394 shows single-agent activity and synergy in combination with PARP inhibitors. A phase Ia clinical trial (NCT05002140) with XRD-0394 in combination with radiotherapy has completed. These results provide a rationale for future clinical trials with XRD-0394 in combination with radiotherapy, PARP inhibitors, and targeted delivery of topoisomerase I inhibitors.
This study was highlighted in the June issue.
Journal: Cancer Research Communications
Exercise-induced β2-adrenergic Receptor Activation Enhances the Antileukemic Activity of Expanded γδ T-Cells via DNAM-1 Upregulation and PVR/Nectin-2 Recognition
Exercise mobilizes cytotoxic lymphocytes to blood which may allow superior cell products to be harvested and manufactured for cancer therapy. Gamma-Delta (γδ) T-cells have shown promise for treating solid tumors, but there is a need to increase their potency against hematologic malignancies. Here, we show that human γδ T-cells mobilized to blood in response to just 20 minutes of graded exercise have surface phenotypes and transcriptomic profiles associated with cytotoxicity, adhesion, migration, and cytokine signaling. Following 14 days ex vivo expansion with zoledronic acid and IL2, exercise mobilized γδ T-cells had surface phenotypes and transcriptomic profiles associated with enhanced effector functions and demonstrated superior cytotoxic activity against multiple hematologic tumors in vitro and in vivo in leukemia-bearing xenogeneic mice. Infusing humans with the β1+β2-agonist isoproterenol and administering β1 or β1+β2 antagonists prior to exercise revealed these effects to be β2-adrenergic receptor (AR) dependent. Antibody blocking of DNAM-1 on expanded γδ T-cells, as well as the DNAM-1 ligands PVR and Nectin-2 on leukemic targets, abolished the enhanced antileukemic effects of exercise. These findings provide a mechanistic link between exercise, β2-AR activation, and the manufacture of superior γδ T-cell products for adoptive cell therapy against hematologic malignancies.
Significance: Exercise mobilizes effector γδ T-cells to blood via β2-adrenergic signaling which allows for generation of a potent expanded γδ T-cell product that is highly cytotoxic against hematologic malignancies.


